请勿第一时间看答案,先自己思考,思考不出来,再看答案
练习题:二叉树的后续遍历
题目描述:
给你一棵二叉树的根节点 root ,返回其节点值的后序遍历 数组。
二叉树的三种遍历方法的考查顺序一致,只是输出顺序不一样:
前序遍历 :遍历到一个节点后,即刻输出该节点的值,并继续遍历其左右子树。输出顺序:根、左、右
中序遍历 :遍历到一个节点后,将其暂存,遍历完左子树后,再输出该节点的值,然后遍历右子树。输出顺序:左、根、右
后序遍历 :考察到一个节点后,将其暂存,遍历完左右子树后,再输出该节点的值。输出顺序:左、右、根
示例1:
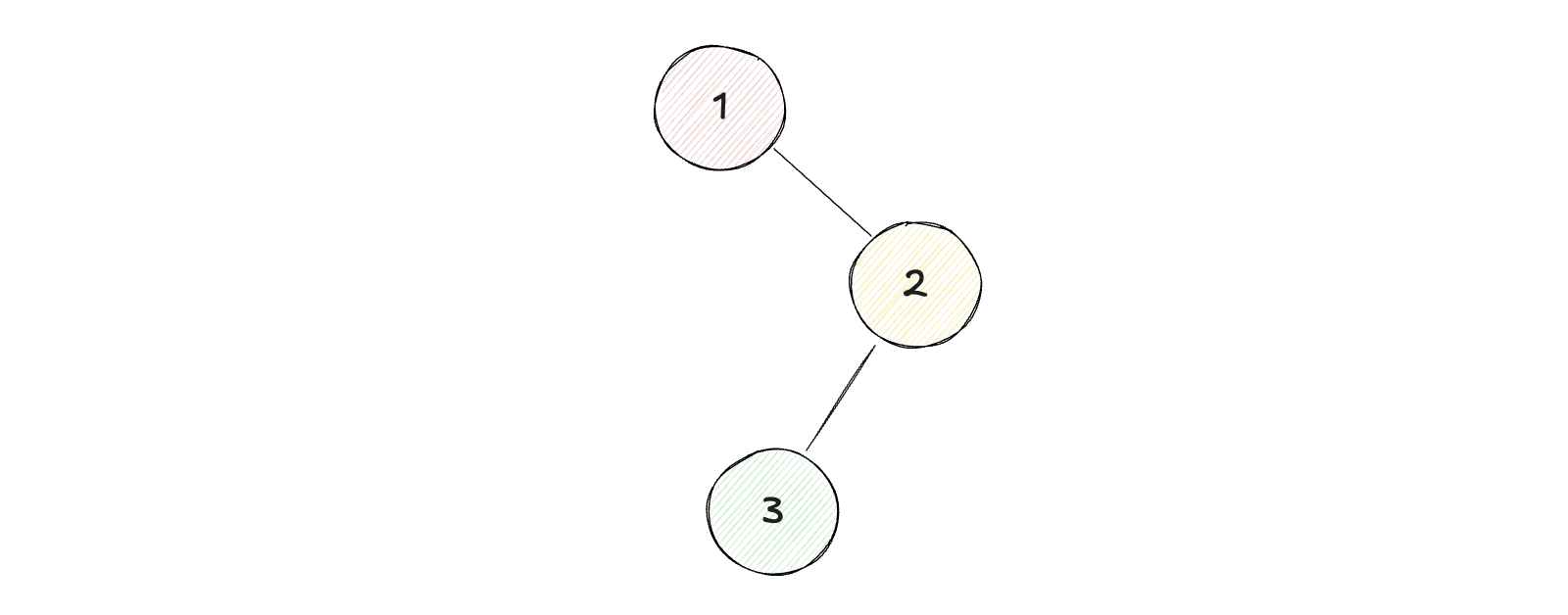
1
输入:root = [1, null, 2, 3]
2
输出:[3, 2, 1]
示例2:
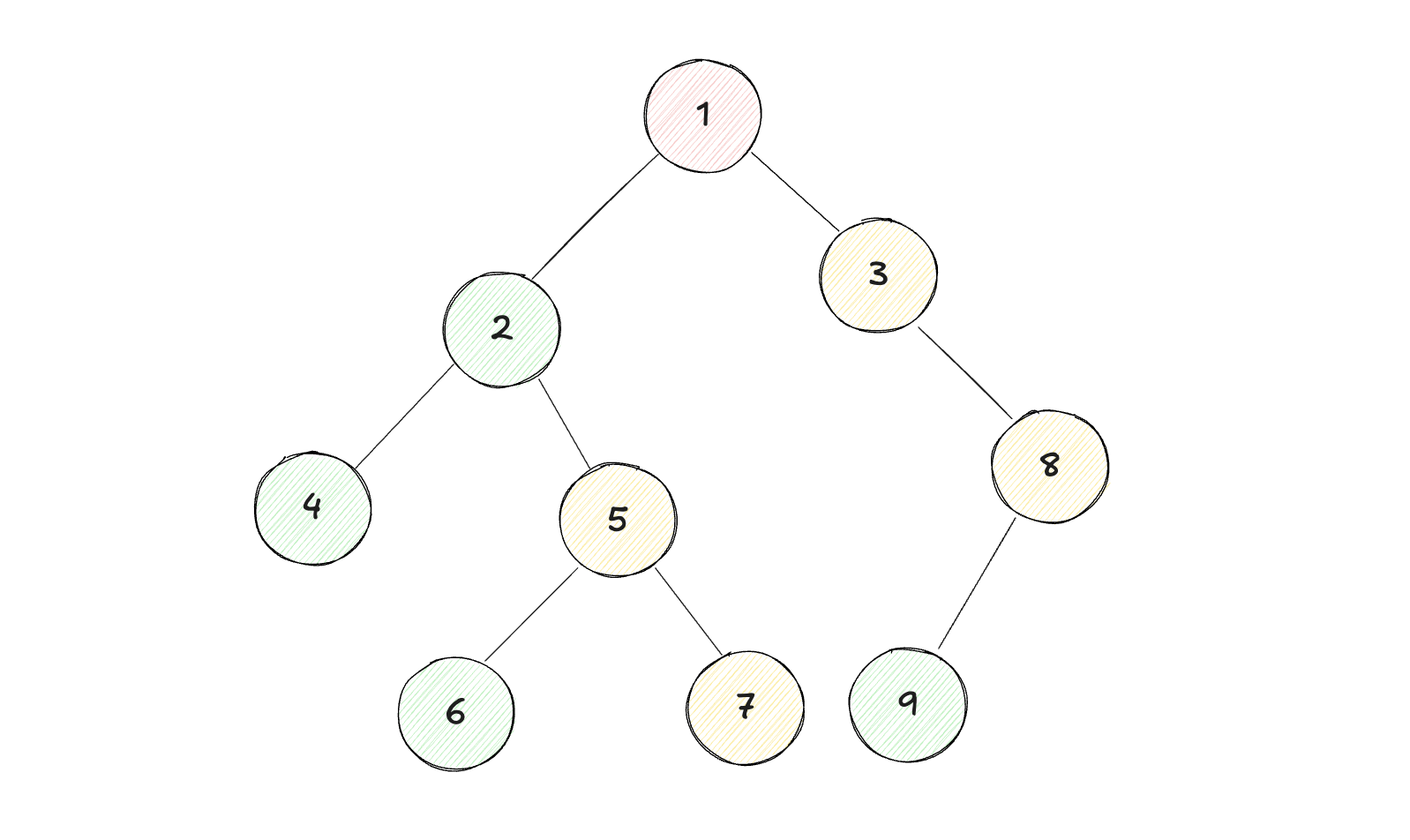
1
输入:root = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, null, 8, null, null, 6, 7, 9]
2
输出:[4, 6, 7, 5, 2, 9, 8, 3, 1]
解题思路
在迭代章节中,我们学习了使用栈来模拟递归的过程。因此,无论是前序遍历、中序遍历还是后序遍历,我们都可以使用栈来实现。并且执行的过程都是一样的,只是输出顺序不同
因此,我们首先依然是定义一个栈数组,用于帮助使用迭代来模拟栈的顺序,然后定义一个结果数组,用于存储输出结果
1
const
stack
:
TreeNode
[]
=
[]
2
const
res
:
number
[]
=
[]
然后需要按照栈的循序依次将节点压入栈中,在判断到节点没有任何子节点之后,再弹出栈中。
10
const
stack
=
[]
20
// 将根节点压入栈中
30
stack.
push
(root)
40
root.x
=
true
// 标记节点是否已经访问过
50
// 遍历栈,遍历的结束条件为栈数组被清空
60
while
(stack.
length
!==
0
) {
70
const
top
=
stack[stack.
length
-
1
]
80
90
// 先左边入栈、再右边入栈
10
if
(top.left
&&!
top.left.x) {
11
stack.
push
(top.left)
12
top.left.x
=
true
13
}
else if
(top.right
&&!
top.right.x) {
14
stack.
push
(top.right)
15
top.right.x
=
true
16
}
else
{
17
// 如果节点没有任何子节点,则弹出栈中
18
stack.
pop
()
19
}
20
}
记录了执行过程之后,表示每个节点实际上我们都执行到位了,我们接下来需要做的就是在合适的时候,把对应的节点值记录到结果数组中。先序是在入栈的时候记录,而后序则是在节点出栈的时候记录。
所以,最终完整的代码如下所示
10
class
TreeNode
{
20
val
:
number
30
left
:
TreeNode
|
null
40
right
:
TreeNode
|
null
50
constructor
(
val
?:
number
,
left
?:
TreeNode
|
null
,
right
?:
TreeNode
|
null
) {
60
this
.val
=
(val
===
undefined
?
0
:
val)
70
this
.left
=
(left
===
undefined
?
null
:
left)
80
this
.right
=
(right
===
undefined
?
null
:
right)
90
}
10
}
11
12
function
preorderTraversal
(
root
) {
13
const
res
=
[]
14
if
(
!
root) {
15
return
res
16
}
17
// 定义栈数组
18
const
stack
=
[]
19
// 将根节点压入栈中
20
stack.
push
(root)
21
root.x
=
true
// 标记节点是否已经访问过
22
// 遍历栈,遍历的结束条件为栈数组被清空
23
while
(stack.
length
!==
0
) {
24
const
top
=
stack[stack.
length
-
1
]
25
26
if
(top.left
&&!
top.left.x) {
27
stack.
push
(top.left)
28
top.left.x
=
true
29
}
else if
(top.right
&&!
top.right.x) {
30
stack.
push
(top.right)
31
top.right.x
=
true
32
}
else
{
33
const
node
=
stack.
pop
()
34
res.
push
(node.val)
35
}
36
}
37
38
return
res
39
};
我的这种思路是严格按照栈的思路来解决的,所以代码比较中规中矩。但是我们可以通过魔改入栈的顺序来简化代码,不过这会带来理解上的困难。其他方式大家可以参考评论区,我这里就不再赘述。
例如,下面这种解法,通过定义一个 current
指针来记录当前节点,在逻辑的控制上,current
指针的移动顺序与栈的顺序一致,然后通过 lastNode
来记录上一次出栈的节点,从而判断当前节点是否有右节点,有则压栈,否则记录节点信息并出栈。
同样在出栈时,按照后序遍历的顺序来记录节点信息。
10
var
postorderTraversal
= function
(
root
) {
20
const
stack
=
[]
30
let
current
=
root
40
let
lastNode
=
null
50
let
result
=
[]
60
while
(stack.
length
||
current){
70
// 压入当前节点
80
if
(current){
90
stack.
push
(current)
10
current
=
current.left
11
}
else
{
12
const
node
=
stack[stack.
length
-
1
]
13
// 取栈顶的节点,判断是否有右节点,有则压栈(注意是否已经遍历过了)
14
if
(node.right
&&
node.right
!==
lastNode) {
15
current
=
node.right
16
}
else
{
17
// 记录节点信息并且出栈
18
result.
push
(node.val)
19
lastNode
=
stack.
pop
()
20
}
21
}
22
}
23
return
result
24
};